Aspiring doctors and dentists of Pakistan, hello! As you stand at the threshold of one of the most critical academic challenges of your life – the Medical & Dental College Admission Test (MDCAT) – one document stands paramount, acting as the bedrock of your entire preparation strategy: the official MDCAT syllabus.
Latest Update – June 10, 2025:
The Pakistan Medical and Dental Council (PMDC) has officially announced the finalized MDCAT syllabus for 2025, providing clarity for students preparing for the upcoming medical entrance examination. This announcement comes after months of deliberation by the PMDC MDCAT Reform Committee, which began reviewing potential changes in November 2024.
First of all, download the PMDC MDCAT 2025 syllabus from the official website of MDCATGURU.COM. Stay aware of other fake websites that are providing the wrong updated syllabus for MDCAT 2025. So, let us evaluate the PMDC Syllabus 2025.

Exam Structure & Key Changes
The MDCAT 2025 introduces several important modifications to the traditional format:
Test Format
- Total MCQs: 180 questions
- Duration: 3 hours
- Format: Paper-based multiple choice
- Marking: No negative marking
- Minimum Pass Marks: 55% for Medical Colleges, 50% for Dental Colleges
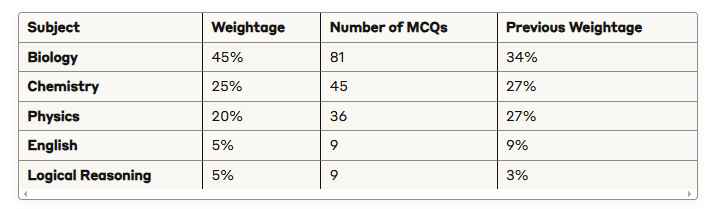
Subject Weightage Distribution
The weightage has been significantly restructured from previous years:
Difficulty Level Distribution
- Easy Questions: 15% (27 MCQs)
- Moderate Questions: 70% (126 MCQs)
- Difficult Questions: 15% (27 MCQs)
Subject-wise Detailed Breakdown
1. BIOLOGY (45% – 81 MCQs)
Biology dominates the MDCAT 2025 with the highest weightage, covering 16 comprehensive units:
Core Units Overview:
Unit 1: Acellular Life
- Virus classification based on structure, strands, diseases, and hosts
- AIDS and HIV infection: symptoms, transmission modes, and causative factors
Unit 2: Bioenergetics
- Cellular respiration of proteins and fats
- Correlation with glucose respiration pathways
Unit 3: Biological Molecules
- Classification and importance of biological molecules
- Water’s biological properties (polarity, hydrolysis, specific heat)
- Carbohydrates: monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides
- Proteins: amino acid structure and protein organization
- Lipids: phospholipids, triglycerides, acylglycerols
- RNA structure and function
- DNA double helix structure (Watson-Crick model)
- Gene definition and function
Unit 4: Cell Structure & Function
- Comparison of animal and plant cells
- Prokaryotic vs eukaryotic cell structures
- Organelles: nucleus, ER, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria
- Chromosome structure and composition
Unit 5: Coordination & Control
- Receptor functions as transducers
- Neuron structure (cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath)
- Nerve impulse and reflex classifications
- Brain anatomy: brain stem, midbrain, cerebellum, cerebrum
Unit 6: Enzymes
- Enzyme characteristics and mechanisms
- Factors affecting enzyme reactions (temperature, pH, concentration)
- Enzyme inhibitors
Unit 7: Evolution
- Origin of life concepts
- Lamarck’s theory of acquired characteristics
- Darwin’s natural selection theory
Unit 8: Reproduction
- Male and female reproductive system functions
- Hormonal regulation of reproductive processes
- Menstrual cycle and hormonal roles
- Sexually transmitted diseases
Unit 9: Support & Movement
- Cartilage, muscle, and bone characteristics
- Muscle types: smooth, cardiac, skeletal
- Skeletal muscle ultrastructure and contraction
- Joint classification and arthritis
Unit 10: Inheritance
- Mendel’s laws of inheritance
- Independent assortment with examples
- Gene linkage and crossing over
- Sex-linked inheritance and hemophilia
Unit 11: Circulation
- Human heart structure
- Cardiac cycle phases
- Blood vessel differences and functions
- Lymphatic system components
Unit 12: Immunity
- Specific defense mechanisms and their importance
Unit 13: Respiration
- Respiratory system functions
- Gas exchange in lungs
- Smoking effects on respiratory system
Unit 14: Digestion
- Digestive system parts and functions
- Associated glands and structures
Unit 15: Homeostasis
- Urinary system organs and kidney structure
- Glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion
- Kidney functions in excretion and osmoregulation
- Kidney stones and failure causes
- Thermoregulation processes
- Nitrogenous waste compounds
Unit 16: Biotechnology
- Vaccine production through biotechnology
- Disease diagnosis using DNA/RNA probes and monoclonal antibodies
- Biotechnology products for disease treatment
2. CHEMISTRY (25% – 45 MCQs)
Chemistry covers 20 comprehensive units spanning both inorganic and organic chemistry:
Inorganic Chemistry Units:
Unit 1: Fundamental Concepts
- Mole ratios and stoichiometric calculations
- Limiting and excess reactants
- Theoretical yield, actual yield, and percentage yield calculations
Unit 2: Atomic Structure
- Proton discovery and properties
- Planck’s quantum theory and photon concept
- Quantum numbers and orbital concepts
- S, P, D orbital shapes
- Electronic configuration using Aufbau, Pauli, and Hund’s principles
Unit 3: Gases
- Kinetic molecular theory postulates
- Standard temperature and pressure (STP)
- Gas laws: Boyle’s, Charles’s, and combined gas laws
- Ideal gas equation derivation and applications
- Real vs ideal gas distinctions
Unit 4: Liquids
- Liquid properties based on kinetic theory
- Evaporation, boiling point, and vapor pressure
- Hydrogen bonding in H₂O, NH₃, and HF
- Water’s anomalous behavior
Unit 5: Solids
- Crystalline solid characteristics
- Factors affecting ionic crystal shapes
- Ionic vs molecular crystals
- Crystal lattice structure and lattice energy
Unit 6: Chemical Equilibrium
- Equilibrium concepts in reversible reactions
- Le Chatelier’s principle applications
- Solubility products and common ion effect
- Buffer solutions and Haber’s process
Unit 7: Reaction Kinetics
- Chemical kinetics definitions
- Rate equations and factors affecting reaction rates
- Reaction order and rate constants
- Activation energy and activated complex
Unit 8: Thermochemistry
- Thermodynamics fundamentals
- Exothermic and endothermic reactions
- System, surroundings, and state functions
- First law of thermodynamics and Hess’s law
Unit 9: Electrochemistry
- Redox reaction characteristics
- Oxidation and reduction in terms of oxidation numbers
- Balancing redox equations
- Standard hydrogen electrode and electrode potentials
Unit 10: Chemical Bonding
- VSEPR theory applications
- Sigma and pi bond features
- Hybridization and molecular shapes
- Dipole moments and molecular polarity
- Bond energy comparisons
Unit 11: S- and P-Block Elements
- Periodic trends: atomic radii, ionization energy, electronegativity
- Periodic table block demarcation
- Group I and II element reactions
- Group IV element reactions
Unit 12: Transition Elements
- Electronic structures of d-block elements and ions
Organic Chemistry Units:
Unit 13: Fundamental Principles
- Organic chemistry definitions and classifications
- Functional group concepts
- Stereoisomerism types
Unit 14: Hydrocarbons
- Alkane nomenclature and free radical mechanisms
- Alkene nomenclature, shapes, and reactivity
- Alkene preparation methods
- Benzene molecular orbital treatment
- Resonance and resonance energy
- Electrophilic substitution mechanisms
- Alkyne nomenclature, preparation, and reactions
Unit 15: Alkyl Halides
- IUPAC nomenclature and structure
- Nucleophilic substitution and elimination mechanisms
Unit 16: Alcohols and Phenols
- Nomenclature, structure, and reactivity
- Ether and ester preparation
- Electrophilic aromatic substitution in phenols
Unit 17: Aldehydes and Ketones
- Nomenclature and structural features
- Preparation methods and reactivity comparisons
- Nucleophilic addition reactions
- Reduction and oxidation reactions
Unit 18: Carboxylic Acids
- Nomenclature, structure, and preparation
- Reactivity patterns
- Conversion to acid derivatives
Unit 19: Macromolecules
- Protein classification and structure-function relationships
- Protein nutritional importance
- Enzymes as biocatalysts
Unit 20: Industrial Chemistry
- Adhesive types and applications
- Dye types and uses
- Polymer classifications
3. PHYSICS (20% – 36 MCQs)
Physics encompasses 16 units covering classical and modern physics concepts:
Mechanics Units:
Unit 1: Vectors and Equilibrium
- Vector addition using rectangular components
- Scalar and vector products
- Angle relationships in vector operations
Unit 2: Force and Motion
- Displacement, velocity, and acceleration concepts
- Displacement-time graph interpretations
- Projectile motion analysis
- Newton’s laws applications
- Momentum conservation and collision analysis
Unit 3: Work and Energy
- Work concept as force-displacement product
- Kinetic and potential energy relationships
- Power as scalar product of force and velocity
- Energy conservation and efficiency
Unit 4: Rotational and Circular Motion
- Angular displacement, velocity, and acceleration
- Linear and angular quantity relationships
Unit 5: Fluid Dynamics
- Terminal velocity and fluid drag
- Fluid flow types and characteristics
- Continuity equation applications
- Bernoulli’s equation and its applications
Wave and Oscillation Units:
Unit 6: Waves
- Wave motion characteristics
- Progressive wave properties
- Sound speed and Newton’s formula
- Laplace correction for sound speed
- Wave interference and superposition
- Stationary wave formation
- Simple harmonic motion principles
Thermodynamics Unit:
Unit 7: Thermodynamics
- Thermal equilibrium and heat transfer
- Molar specific heat concepts
- First law of thermodynamics
- Work calculations in volume changes
Electricity and Magnetism Units:
Unit 8: Electrostatics
- Coulomb’s law applications
- Electric field concepts and calculations
- Electric potential and potential energy
- Capacitor charging and discharging
Unit 9: Current Electricity
- Steady current concepts
- Ohm’s law and resistance factors
- Internal resistance and maximum power transfer
Unit 10: Electromagnetism
- Magnetic flux density and flux concepts
- Charged particle motion in magnetic fields
Unit 11: Electromagnetic Induction
- Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction
- Lenz’s law and energy conservation
- Transformer construction and operation
Unit 12: Alternating Current
- AC phase relationships
- AC behavior through resistors, capacitors, and inductors
- Electromagnetic spectrum overview
Electronics and Modern Physics Units:
Unit 13: Electronics
- Rectification processes
- PN junction characteristics and biasing
Unit 14: Dawn of Modern Physics
- Quantum theory and photon energy concepts
Unit 15: Atomic Spectra
- Atomic and line spectra descriptions
Unit 16: Nuclear Physics
- Atomic nucleus composition
- Nuclear decay characteristics
- Half-life calculations
- Radiation’s biological and medical applications
4. ENGLISH (5% – 9 MCQs)
English assessment focuses on three core competency areas:
Reading and Thinking Skills
- Scanning techniques for short question answers
- Contextual meaning deduction
- Analysis of figurative language and sensory appeals
Formal and Lexical Language Aspects
- Contextual vocabulary understanding
- Synonym usage for irony, parody, and satire
- Grammar components:
- Pronoun-antecedent agreement
- Tense usage
- Infinitive and gerund phrases
- Adverb positioning
- Preposition usage
- Transitional devices
- Punctuation marks
- Sentence structure analysis
- Active and passive voice
- Direct and indirect speech
Writing Skills
- Proofreading and editing techniques
- Faulty sentence structure identification
- Subject-verb agreement
- Error correction in usage and style
5. LOGICAL REASONING (5% – 9 MCQs)
Logical reasoning introduces six thematic areas:
Critical Thinking
- Logical argument development
- Truth and falsehood evaluation
- Belief system analysis using logical reasoning
Letter and Symbol Series
- Sequential pattern recognition
- Mathematical operation applications
- Alphabetical order progressions
Logical Deductions
- Statement relationship analysis
- Structured thinking for conclusion drawing
- Information-based prediction skills
Logical Problems
- Puzzle-solving through deductive reasoning
- Information piece integration for problem solving
Course of Action
- Administrative decision-making skills
- Information gathering and analysis
- Action plan evaluation through arguments
Cause and Effect
- Event relationship analysis
- Causal reasoning development
- Argument-based belief validation
Preparation Strategy Recommendations
Subject Priority Allocation
Given the weightage distribution, students should allocate study time as follows:
- Biology: 45% of total study time
- Chemistry: 25% of total study time
- Physics: 20% of total study time
- English & Logical Reasoning: 10% of total study time
Key Preparation Points
- Biology Focus: Emphasize human physiology, genetics, and molecular biology
- Chemistry Balance: Equal attention to inorganic concepts and organic mechanisms
- Physics Applications: Stress problem-solving in mechanics and electricity
- English Proficiency: Practice grammar rules and contextual comprehension
- Logical Reasoning: Develop pattern recognition and analytical thinking
Difficulty Level Strategy
- Master moderate-level concepts first (70% of questions)
- Build confidence with easy questions (15% of questions)
- Gradually tackle difficult concepts (15% of questions)
This comprehensive syllabus represents PMDC’s commitment to standardizing medical education entry requirements across Pakistan, ensuring equal opportunities for all candidates regardless of their educational backgrounds.
Weaving the Syllabus into Your Daily Study Routine
Knowing the syllabus isn’t enough; you must actively use it.
- The Syllabus as Your Checklist: Print the syllabus. As you complete studying and practicing a topic, check it off. This provides a visual overview of your progress and highlights remaining areas.
- Mapping Resources: Take your primary textbooks (e.g., Punjab Board) and prep materials. For each topic in the syllabus, note down the corresponding chapter/page numbers in your resources. This creates a personalized index.
- Prioritization: If the syllabus or exam pattern provides weightage, use it to allocate study time proportionally. Even without explicit weightage, prioritize topics you find challenging or that appear frequently in past papers (always cross-referenced with the current syllabus).
- Syllabus-Driven Revision: Base your revision plan directly on the syllabus topics. Ensure each point is covered during multiple revision cycles.
- Practice Test Alignment: When choosing practice tests (topic-wise or full-length), check if they align with the scope and topics defined in the official MDCAT syllabus 2025.
Decoding Learning Objectives: Understanding Depth
If your official syllabus includes ‘Learning Objectives’ or uses specific verbs (Define, Identify, Explain, Compare, Contrast, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate), pay close attention!
- Define/Identify: Usually requires recall of facts or definitions.
- Explain/Compare/Contrast: Requires deeper understanding and ability to articulate relationships.
- Apply/Calculate: Requires using formulas or concepts to solve problems.
- Analyze/Evaluate: Requires higher-order thinking, breaking down information, or assessing arguments. This helps gauge the level of mastery expected for each syllabus point.
Avoiding Syllabus-Related Pitfalls
Steer clear of these common mistakes:
- Using an Outdated Syllabus: The #1 error. Always use the official version for your exam year (2025).
- Relying on Unofficial Summaries: These can omit crucial details or contain errors. Refer to the full, official document.
- Ignoring ‘Minor’ Topics: Cover all topics listed in the syllabus, even those that seem less important. Easy marks can be lost here.
- Not Integrating Syllabus with Practice: Simply reading the syllabus isn’t useful. Apply it daily to guide your study and practice.
- Assuming Past Paper Topics = Current Syllabus: Past papers guide style, but the official 2025 syllabus dictates content. Always verify.
Syllabus + Past Papers: A Powerful Combination
Use the syllabus and past papers synergistically:
- Identify a topic in the official 2025 syllabus.
- Study that topic thoroughly from your textbooks.
- Find relevant questions on that topic in recent past papers.
- Analyze how the topic is typically tested (conceptual vs. numerical, common tricks).
- This informs your preparation focus for that syllabus point.
Conclusion: Your Syllabus, Your Success
The official MDCAT syllabus 2025 is far more than a bureaucratic document; it is the fundamental key unlocking focused, efficient, and effective preparation. It’s the architectural plan upon which you will build your success story. From Lahore to Karachi, Quetta to Peshawar, every successful MDCAT candidate shares one trait: a thorough understanding and diligent application of the official syllabus.
Make it your mission to download the official MDCAT syllabus 2025 from the PM&DC website the moment it becomes available. Dissect it, understand it, and let it guide every step of your preparation journey. Map your resources to it, use it as your daily checklist, and align your practice with its scope.
Mastering the MDCAT syllabus is the first, non-negotiable step towards achieving your dream of entering Pakistan’s esteemed medical and dental colleges. Embrace it, conquer it, and pave your way to success!
(Disclaimer): Information regarding the MDCAT syllabus structure and specific topics is based on typical patterns observed in previous years. It is essential to obtain and rely solely on the official MDCAT syllabus 2025 as released by the Pakistan Medical & Dental Council (PM&DC) for definitive information regarding your examination scope and content. Regularly check official sources for updates.
Checkout our WARRIORS Test Series that is absolutely FREE for every student.
The MDCAT 2025 syllabus comprises five subjects: Biology, Chemistry, Physics, English, and Logical Reasoning.
You can download the official MDCAT 2025 syllabus PDF from the PMDC website or educational portals like mdcatguru.com
The subject-wise weightage for MDCAT 2025 is as follows: Biology (34%, 68 MCQs), Chemistry (27%, 54 MCQs), Physics (27%, 54 MCQs), English (9%, 18 MCQs), and Logical Reasoning (3%, 6 MCQs).
The MDCAT 2025 syllabus has been reviewed to ensure alignment with existing recognized syllabi. Any updates or modifications are communicated promptly by PMDC.
No, there is no negative marking in the MDCAT 2025 exam.
The MDCAT 2025 exam duration is 3.5 hours.
The MDCAT 2025 exam consists of a total of 200 multiple-choice questions.
The minimum passing marks for medical college admission are 65%, and for dental college admission, it is 55%.
Subject-wise details and downloadable PDFs for the MDCAT 2025 syllabus are available on educational websites like mdcatguru.com.
The Logical Reasoning section assesses critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Practice with relevant exercises and past papers to enhance performance in this section.



vishan Das
hi sir
let me join 🙂
Saleem Ijaz
How to focus on MDCAT preparation Give your suggestions!
aiza bukhari
behtareen breakdown of pmdc mdcat 2023 syllabus.. apki web bht useful hai mdcat students k liye.. jazakAllah 🫀
sani
mdcat 2023 test 2022 waly se tough ho ga ya easy?
nemo
sir official download hai ye? pmdc syllabus 2023
Harmainy khan
Assalam o Alaikum I have a question plz any one can answer If the students belongs to Sindh province, which books should they read? Only Sindh Province or Punjab and Federal too ??
Malka
If i want to know topics in chapters for mdcat..e.g.force and motion is chapter,so which topics will be included in it?So ,how can i find these topics?
Faizaabbasi
I want to attempt test without academy so I need a supportive notes
kastuk
you can use mine
Noor ul huda
kya ye same topic sindh kay mdcat kay liyay hay us kay liyay to sindh board perhna hay na
Minahil nazeer
Can I join now????
Muhammad Kashif
Hi , please add me in this group.
MDCAT GURU
Kindly check: https://mdcatguru.com/mdcat-whatsapp-group/
Muhammad Kashif
Will MCQS be daily based?
MDCAT GURU
You mean MCQs that we share in WhatsApp channel? If yes then yes! We regularly upload MCQs.
Aziz
Add me in watsapp groups where mcqs sending
MDCAT GURU
Find links here: https://mdcatguru.com/mdcat-whatsapp-group/
Hadi
I want to know that we only have to prepare the topics and subtopics mentioned in the syllabus or whole chapter ?
MDCAT GURU
whole units
Ahsan
Mdcat prepation tips
Dua
Mary Fsc m 75 percentage hai tu main test dysakty ho
Sir
No beta
Shafia Zohra
It is a very excellent site where students can study well and score best in MDCAT
Rabia saad
Sir I am bannu board topper.i have a question that whether we have to cover the extra topics or not.in order to get the position in mdcat
Mahnoor
What is final date of mdcat test
Mahnoor
This sallebus is correct??
Jagarta
I want to join
MDCAT GURU
https://mdcatguru.com/mdcat-whatsapp-group/
RABEEZA
Is MDCAT being conducting provincially ?
MDCAT GURU
yes!
join on whatsapp: https://mdcatguru.com/mdcat-whatsapp-group/
Ahmad
Please share hurry gaseous exchange MDCAT MCQs